Data is a valuable asset for anyone so taking regular backups is important to secure it from any unforeseen data loss.
While individual users use external hard drives or cloud-based services to create data backups, this is not really a viable option for enterprises and large-scale business units.
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is system of scalable storage solution used for storing data across multiple storage drives connected together. It is mainly used for protecting data in case of an unforeseen data loss and increasing data availability. It can be configured in various levels or configuration like 0, 1, 5, 6, 10 and more.
RAID 10 is a storage technology that combines the performance of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1, where the data is spread across multiple disks in a RAID array and creates an exact copy of the data on two or more disks. This provides data redundancy in case of a disk failure. However, RAID 10 is not immune to failure. If one or more drives in a RAID 10 array fail, data loss can occur.
Before moving onto RAID 10 data recovery, let’s understand what RAID 10 is and how data loss occurs in it.
Table of Contents
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 (stripping and mirroring) technology. For more clarification on stripping and mirroring technology in RAID 10, stripping is a technique that divides data into equal blocks and distributes them across multiple disks. This improves performance by allowing multiple read and write operations to occur simultaneously.
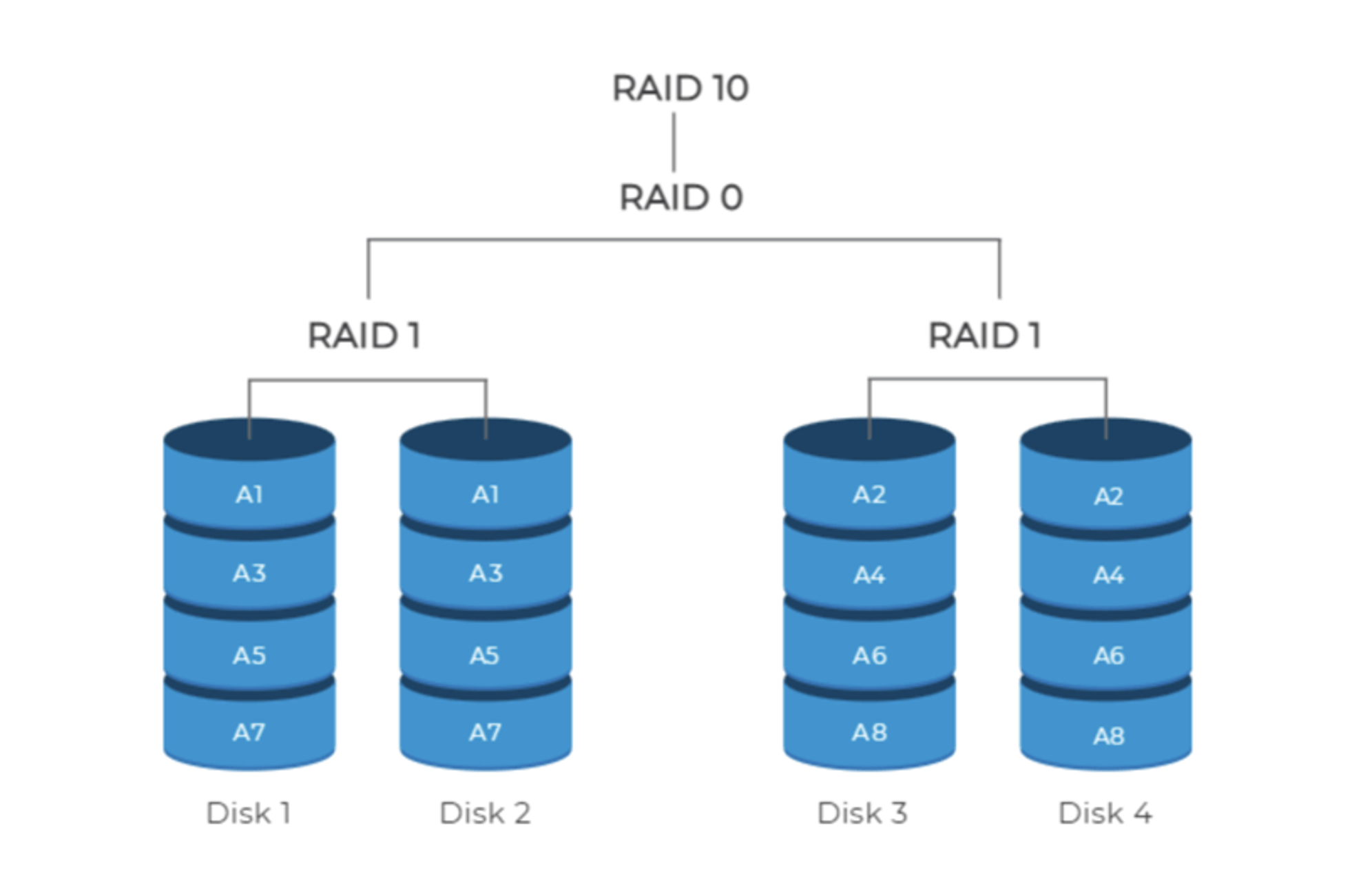
Mirroring in RAID 10 creates a duplicate of each block of data on two or more separate disks. This provides redundancy and protects data from loss in the event of a disk failure.
RAID 10 combines the benefits of striping and mirroring to provide both high performance and data redundancy. It is a good choice for applications where both performance and data protection are critical, such as database servers and file servers.
To set up RAID 10 you’ll need at least 4 drives paired as 2.
Although this solution helps prevent data loss, it has its own pros and cons. Here are a few of them:
| PRO | CONS |
| Fast Read/Write speeds | Expensive |
| High degree of dependability | The set-up process is laborious |
| Compared to other RAIDs, RAID 10 has low latency |
Reasons for RAID Data Loss in RAID 10
RAID 10 is designed to protect your data by copying all of the data on multiple drives in case one of the drives fails. But, unfortunately, RAID 10 is also susceptible to failure. Here are a few reasons why RAID 10 fails:
- Voltage surge or power failure.
- Corruption in the operating system
- Too many bad sectors
- Malware or Virus Attack
- RAID controller malfunctioned
- The logical structure of the disk is damaged
- Human error
Methods to Perform RAID 10 Data Recovery
Firstly, you need to determine if a single disk failed in your RAID 10 array or multiple. If it is a single-drive failure, it is much easier to restore and rebuild data on a hot disk drive. If multiple drives fail, then the process of restoring data from them is a bit grueling.
Keep reading as we show you how to restore data from a single or multiple drives that failed on your RAID 10 array.
Case 1: Single-Disk Failure
If a single drive fails in RAID 10, the RAID array will remain functional, but it will be in a degraded state. This means that the array is more vulnerable to further disk failures, as the redundancy provided by the mirrored pairs is compromised.
At this moment, you should replace the failed drive with a working spare hot disk drive immediately, and once installed, the controller will rebuild and recover all the lost data on the newly installed hot disk drive.
In case you don’t have a hot disk drive to install, you can install a new drive and manually initiate the RAID 10 data rebuild process.
Here’s how:
- Open the “iprconfig utility” by typing “iprconfig.”
- Select “Work with disk unit recovery” option.
- Choose “Rebuild disk unit data.”
- Now, select the disk/s you want to rebuild and press “Enter” on your keyboard.
- Press “Enter” to rebuild data q to cancel the process
Case 2: Multiple Disk Failure
If multiple drives fail in a RAID 10 array, i.e., when both disks fail in one or more sets that are mirrored, the status of the disk array changes to “Failed.”
Here’s what you can do if your RAID 10 array fails:
- Stop using it right away
- Get rid of the current disk array
- Rebuild the disk array by replacing the failed disks
Once done, restore the file system and rebuild the disk array by copying all the data from a backup drive to the newly installed disk array from your failed RAID 10 arrays.
If you want to restore your data from failed RAID 10, use a third-party tool that supports data recovery from RAID data recovery from RAID 10, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician, which supports RAID data recovery from inaccessible or corrupted RAID 10.

Conclusion
RAID 10 is a popular RAID configuration that provides data protection while offering high performance. However, even RAID 10 arrays can fail due to issues like power failure, bad sectors, and other reasons, and when they do, RAID data loss can occur.
To restore lost RAID recovery from a RAID 10 array, there are a few things you can do to try to recover it. First, you should check to see if the RAID controller has any diagnostic tools that can help you identify the problem.
If the RAID controller is unable to repair the array, use reliable third-party RAID data recovery software to recover all of your data successfully.




